NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed! Hydrogen leaks halt SLS fueling test—NASA targets early March 2026 for historic crewed Moon flyby. Why the delay and what’s next for astronauts?
Just months before launch, NASA discovered a critical issue that could have jeopardized its first crewed lunar mission in over 50 years.

NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed what’s Next?
Space exploration has always been a thrilling mix of triumphs and setbacks, reminding us that pushing the boundaries of human capability isn’t without its challenges. Just when excitement was building for NASA’s Artemis II mission—a groundbreaking crewed flyby around the Moon—the agency announced a delay. Originally eyeing a February 2026 launch window, the mission has now been postponed to no earlier than early March. The culprit? Persistent hydrogen leaks in the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, uncovered during recent wet dress rehearsals and testing. As engineers scramble to make on-pad repairs, this hiccup underscores the complexities of sending humans back to lunar orbit for the first time since the Apollo era.
For those following NASA’s ambitious Artemis program, this news might feel like a familiar echo. The program aims to return humans to the Moon and lay the groundwork for future Mars missions, but technical hurdles have been part of the journey from the start. Let’s dive deeper into what happened, why it matters, and what it means for the future of space travel.
Understanding the Delay: What Went Wrong with the SLS Rocket?
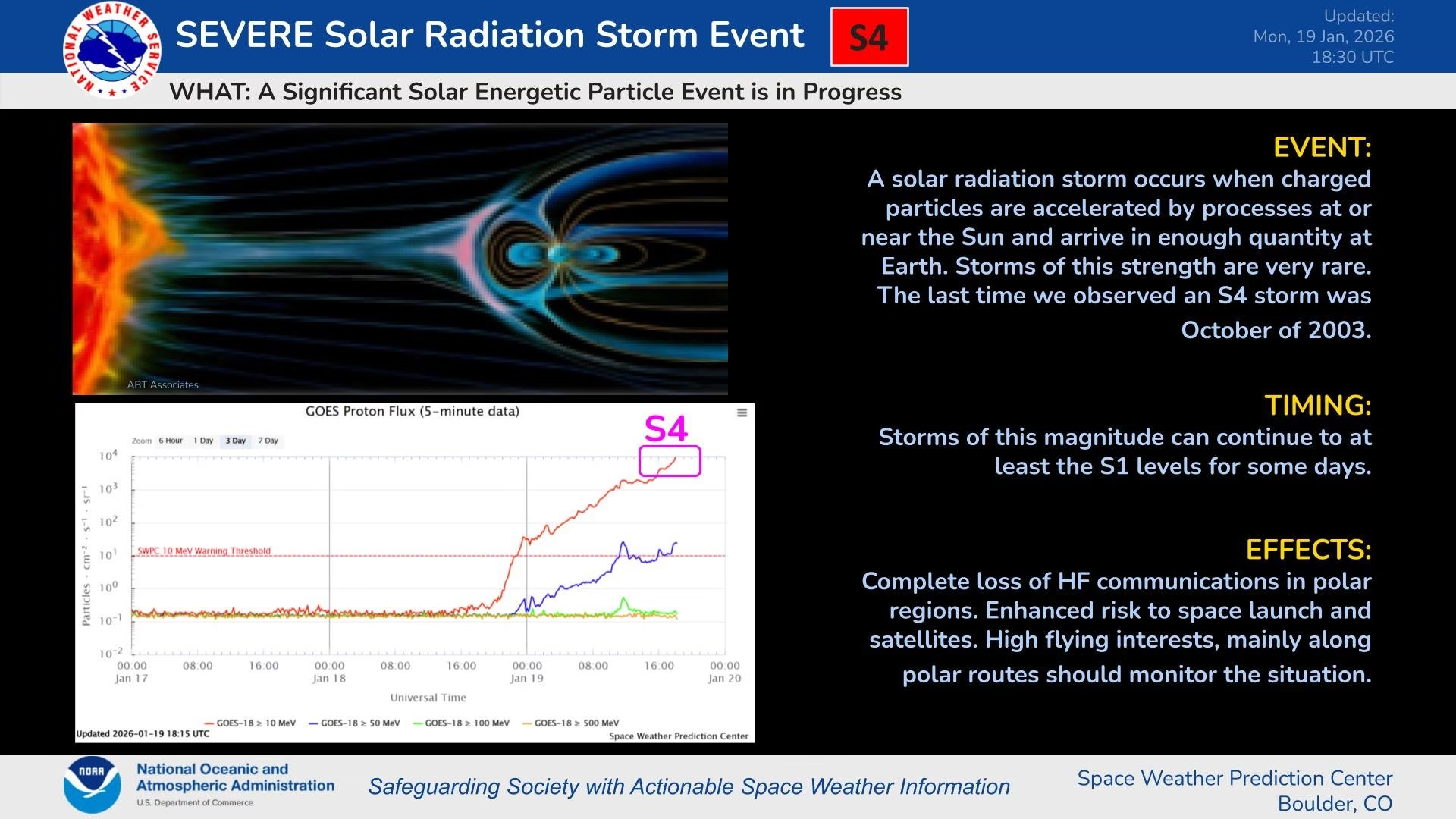
The Space Launch System, or SLS, is NASA’s powerhouse rocket designed specifically for deep-space missions. Standing at over 300 feet tall, it’s the most powerful rocket the agency has built since the Saturn V of the Apollo days. But power comes with precision demands, especially when dealing with cryogenic propellants like liquid hydrogen and oxygen, which are stored at ultra-low temperatures to keep them in liquid form.
During a critical wet dress rehearsal—a full simulation of launch day procedures, including fueling the rocket—engineers encountered leaks in the liquid hydrogen system. This test, conducted at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, involved loading the SLS with hundreds of thousands of gallons of propellant. Things started smoothly, but as the countdown progressed, a leak appeared in the quick-disconnect interface, a key connection point that routes hydrogen into the rocket’s core stage and NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed.
Teams spent hours troubleshooting, stopping the flow to warm up the seals and reseat them, then resuming. They managed to fully fuel the rocket and push the simulated countdown to about T-minus 5 minutes. But then, a spike in the leak rate triggered an automatic stop by the ground launch sequencer. It was a safety measure, but it meant the test couldn’t be completed as planned. Additionally, a valve issue popped up on the Orion spacecraft atop the SLS, adding another layer of complexity.
This isn’t the first time hydrogen leaks have plagued the SLS. Back in 2022, during preparations for the uncrewed Artemis I mission, similar issues delayed launch multiple times just like this NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed. NASA thought they’d learned from those experiences, implementing fixes like better sealing techniques and procedural adjustments. Yet, here we are again, three years later, facing the same gremlins. Why? Experts speculate it could be due to the extreme conditions—hydrogen is notoriously tricky because it’s the smallest molecule, prone to slipping through tiny gaps, especially under pressure and cold. Material fatigue or subtle manufacturing variances might also play a role.
The decision to delay came swiftly after the test. NASA needs time to analyze data, make repairs right there on the launch pad, and likely conduct another wet dress rehearsal to verify everything’s solid. Pushing to March gives them that breathing room without rushing safety. After all, this mission isn’t just about hardware; it’s carrying four human lives.
A Quick Refresher: What Is the Artemis II Mission?
If you’re new to the Artemis saga or need a reminder, let’s break it down. Artemis II is the second major flight in NASA’s Artemis program, following the successful uncrewed Artemis I in 2022, which tested the SLS and Orion in a lunar orbit. This time, it’s crewed, marking the first time astronauts will fly aboard the Orion spacecraft in deep space.
The mission’s core objective? A 10-day lunar flyby to test systems with humans on board. The crew will launch from Kennedy Space Center, orbit Earth a few times to check out Orion’s life support, navigation, and communication systems, then slingshot toward the Moon on a free-return trajectory. They’ll loop around the far side of the Moon—getting as close as about 4,600 miles—before heading back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
No landing this time; that’s for Artemis III and beyond. But Artemis II is crucial for validating that Orion can keep astronauts safe far from Earth, where real-time help from Mission Control isn’t instantaneous due to communication delays. It’s a stepping stone to sustainable lunar presence and, eventually, boots on Mars.
Meet the Crew: Pioneers of the Artemis Generation
One of the most exciting aspects of Artemis II is its diverse crew, announced back in 2023. Leading the charge is Commander Reid Wiseman, a veteran NASA astronaut with experience from the International Space Station (ISS). He’ll be joined by Pilot Victor Glover, who made history as the first Black astronaut to pilot a spacecraft on this mission type, and Mission Specialist Christina Koch, who holds the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman. Rounding out the team is Jeremy Hansen from the Canadian Space Agency, making this an international effort and highlighting Canada’s contributions to the program.
These four have been in intense training for years, including simulations in Orion mockups, zero-gravity flights, and even quarantine protocols leading up to launch. They’re not just passengers; they’ll conduct scientific experiments en route, studying how deep space affects the human body—from sleep patterns and stress levels to immune system changes and microbiome shifts. Tools like wearable wristbands will track data, helping refine health protocols for longer missions.
Imagine being one of them: Strapped into Orion, hurtling through space at thousands of miles per hour, with Earth shrinking in the rearview and the Moon looming ahead. It’s the stuff of dreams, but also a reminder of the risks involved.
The Bigger Picture: Implications for NASA’s Moon-to-Mars Ambitions
Delays like this aren’t uncommon in space exploration—think of the multiple scrubs for Artemis I or the years of setbacks for the James Webb Space Telescope. But they do raise questions about timelines and costs. The Artemis program, with its goal of landing the first woman and first person of color on the Moon by Artemis III (targeting 2027 or later), relies on SLS and Orion performing flawlessly.
This hydrogen leak issue could point to systemic challenges with the SLS design. Critics argue the rocket, which repurposes some Space Shuttle tech, might be outdated compared to reusable options like SpaceX’s Starship. NASA, however, defends it as a proven heavy-lift vehicle essential for crewed deep-space ops. The delay might add millions to the budget, but safety trumps speed every time.
On the positive side, resolving these leaks now prevents potential disasters in flight. It also gives more time for international partners, like the European Space Agency providing Orion’s service module, to fine-tune their contributions. And let’s not forget the inspiration factor: Artemis is about building a lunar economy, mining resources, and setting up habitats. A successful II paves the way for that.
What’s Next: Repairs and Road Ahead
After announcing NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed Engineers are already at work on the pad, inspecting the quick-disconnect and seals. They might replace components or apply new sealing methods learned from Artemis I. Once fixed, expect another wet dress to confirm readiness. Potential launch windows in early March include dates like March 6-9 or 11, depending on orbital mechanics and weather.
In the meantime, the crew remains in good spirits, using the extra time for more simulations. NASA emphasizes that this delay is a sign of their commitment to “go when ready,” not on a forced schedule.
As we wait, it’s a great time to reflect on how far we’ve come since Apollo 17 in 1972. Artemis II isn’t just a mission; it’s a bridge to a multi-planetary future. Stay tuned—space is calling, and delays are just part of the adventure.
FAQs About the NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed
1. What is the Artemis II mission?
Artemis II is NASA’s first crewed mission in the Artemis program, sending four astronauts on a 10-day flyby around the Moon to test the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft in deep space.
2. Why was the NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed?
The delay stems from hydrogen leaks in the SLS rocket’s fueling system, discovered during a wet dress rehearsal. Engineers need time for repairs and further testing.
3. When is the new launch date after NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed ?
No earlier than early March 2026, with potential windows around March 6-11.
4. Who are the astronauts on Artemis II?
The crew includes NASA Commander Reid Wiseman, Pilot Victor Glover, Mission Specialist Christina Koch, and CSA’s Jeremy Hansen.
5. Has this happened before?
Yes, similar hydrogen leaks delayed the Artemis I mission in 2022. NASA is applying lessons learned but facing recurring challenges.
6. What are the mission’s main objectives?
To verify Orion’s systems with crew aboard, conduct health studies, and prepare for future lunar landings.
7. How does NASA’s Artemis II launch postponed affect the overall Artemis program?
It pushes back timelines slightly but ensures safety, which is key for subsequent missions like Artemis III’s lunar landing.
8. Is the mission still on track for Mars goals?
Absolutely. Artemis II is a vital test bed for technologies needed for Mars exploration in the 2030s.
9. Can the public watch the launch?
Yes, NASA will provide live streams, and viewing spots near Kennedy Space Center are popular for in-person spectators.
10. Why is hydrogen so problematic in rockets?
It’s extremely cold and small-molecule, making it hard to contain without leaks in seals and interfaces under high pressure.
https://spacetime24.com/artemis-ii-launch-delayed-by-weather/







 The Incredible Legacy of Sunita Williams: NASA astronaut Sunita Williams inside the International Space Station, where she spent a combined 608 days in orbit.
The Incredible Legacy of Sunita Williams: NASA astronaut Sunita Williams inside the International Space Station, where she spent a combined 608 days in orbit.